


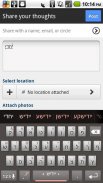
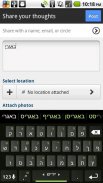
Yiddish Keyboard Plugin

Описание Yiddish Keyboard Plugin
Yiddish Dictionary plugin for Multiling O Keyboard autocorrect and word prediction
Instruction:
⑴ Install this plugin and Multiling O Keyboard. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=kl.ime.oh
⑵ Run O Keyboard and follow its setup guide.
⑶ Slide space bar to switch languages.
If you have font issue, read this: <a href="https://www.google.com/url?q=https://www.google.com/url?q%3Dhttp://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html%26sa%3DD%26usg%3DAFQjCNG71Nl5i6QMcdEZvU1BqM2L70OWlQ&sa=D&usg=AFQjCNHJAfktVVilzCrduIwvK96EQvYRGw" target="_blank">http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html</a>
Wikipedia:
Yiddish (ייִדיש, יידיש or אידיש, yidish/idish, literally "Jewish") is the historical language of the Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the pre-existing language of the nascent Ashkenazi community with an extensive Germanic based vocabulary. Yiddish is written with a fully vocalized alphabet based on the Hebrew script.
The earliest surviving references date from the 12th century and call the language לשון־אַשכּנז (loshn-ashknez = "language of Ashkenaz") or טײַטש (taytsh), a variant of tiutsch, the contemporary name for Middle High German. In common usage, the language is called מאַמע־לשון (mame-loshn, literally "mother tongue"), distinguishing it from Hebrew and Aramaic, which are collectively termed לשון־קודש (loshn-koydesh, "holy tongue"). The term "Yiddish" did not become the most frequently used designation in the literature until the 18th century. In the late 19th and into the 20th century the language was more commonly called "Jewish", especially in non-Jewish contexts, but "Yiddish" is again the more common designation.
Modern Yiddish has two major forms. Eastern Yiddish is far more common today. It includes Southeastern (Ukrainian–Romanian), Mideastern (Polish–Galician–Eastern Hungarian), and Northeastern (Lithuanian–Belarusian) dialects. Eastern Yiddish differs from Western both by its far greater size and by the extensive inclusion of words of Slavic origin. Western Yiddish is divided into Southwestern (Swiss–Alsatian–Southern German), Midwestern (Central German), and Northwestern (Netherlandic–Northern German) dialects. Yiddish is used in a large number of Orthodox Jewish communities worldwide and is the first language of the home, school, and in many social settings among most Hasids. Yiddish is also the academic language of the study of the Talmud according to the tradition of the Lithuanian yeshivas.
The term Yiddish is also used in the adjectival sense, synonymously with Jewish, to designate attributes of Ashkenazi culture (for example, Yiddish cooking and Yiddish music).[4]
</div> <div jsname="WJz9Hc" style="display:none">Идиш словарь плагин для вывода клавиатуры, многоязычный автозамены и прогнозирования слова
Инструкция:
⑴ установить этот плагин и многоязы вывода клавиатуры. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=kl.ime.oh
⑵ Выполнить О Клавиатура и следить за его руководство по настройке.
⑶ пробел Презентация для переключения языков.
Если у вас есть вопрос шрифта, прочтите это: <a href="https://www.google.com/url?q=http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html&sa=D&usg=AFQjCNG71Nl5i6QMcdEZvU1BqM2L70OWlQ" target="_blank">http://honsoapps.appspot.com/1/ma.html</a>
Википедия:
Идиш (ייִדיש, יידיש или אידיש, yidish / idish, буквально «еврейский») является историческим языком ашкеназских евреев. Она возникла в 9 веке в Центральной Европе, обеспечивая уже существующие язык зарождающейся общины ашкенази с обширной германской основе словаря. Идиш написано с полностью озвучены алфавита на основе сценария иврите.
Самые ранние из сохранившихся ссылки датируются 12-м веке и вызвать язык לשון-אַשכּנז (лошн-ashknez = "язык Ашкеназе") или טייַטש (taytsh), вариант tiutsch, современное название для Ближнего Верховного немецком языке. В обиходе, язык называется מאַמע-לשון (маме-лошн, буквально "родной язык"), отличающие его от иврите и арамейском, которые в совокупности называются לשון-קודש (лошн-koydesh, "святой язык"). Термин "идиш" не стал наиболее часто используется обозначение в литературе до 18-го века. В конце 19-го и в 20-м веке язык чаще называют "еврейским", особенно в нееврейских контекстах, но "идиш" снова чаще обозначение.
Современный идиш имеет две основные формы. Восточная идиш гораздо более распространены сегодня. Она включает в себя Юго-Восточной (украинский-румынский), ближневосточного (польско-галицко-Восточная венгерский), и Северо-Восточной (литовско-белорусские) диалекты. Восточная идиш отличается от западной как по своей гораздо большей размера и обширной включения слов славянского происхождения. Западная идиш делится Юго-Западного (швейцарский эльзасском Южный немецкий), Среднем Западе (Центральная немецкий), и Северо-Западного (Netherlandic-Северная немецкий) диалектов. Идиш используется в большом количестве православных еврейских общин по всему миру и является первым языком в семье, школе, и во многих общественных местах среди большинства хасидов. Идиш также академический язык изучения Талмуда по традиции литовской иешивы.
Термин идиш также используется в прилагательных смысле, как синоним еврей, чтобы назначить атрибуты Ашкенази культуры (например, идиш и на идиш приготовления музыки). [4]</div> <div class="show-more-end">
























